Open Information Warehouse and Information Systems in SAP :
Information systems in SAP R/3 are components of SAP's Open Information Warehouse (OIW) framework.
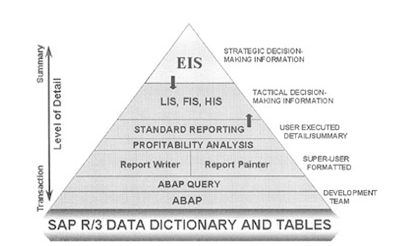
Individual information systems-LIS, FIS, HIS, and so on-in SAP R/3 are limited to a specific application area and associated data objects, except the EIS. These information systems provide an effective method of retrieving summarized data. Following are the major information systems in R/3:
-
Executive Information System (EIS)
-
Logistics Information System (LIS)
-
Financial Information System (FIS)
-
Human Resources Information System (HIS)
Granularity of data available in information systems depends on the type of reporting environment selected. At the EIS level, you access summarized information that can go horizontally across one or more application modules. In other information systems, you are limited to only one application area at a time.
Logistics Information System (LIS)
The LIS is widely used by R/3 customers and plays a major role in preparing information for SAP BW. It consists of the following sub-information systems (the list may vary based on the SAP R/3 OLTP release):
-
Sales Information System (SIS)
-
Purchasing Information System (PIS)
-
Inventory Controlling (INVCO)
-
Shop Floor Information System (SFIS)
-
Plant Maintenance Information System (PMIS)
-
Quality Management Information System (QMIS)
-
Retail Information System (RIS)
-
Warehouse Management Information System (WMIS)
-
Transportation Information System (TIS)
R/3 transaction tables and LIS information structures are updated in two modes: synchronous and asynchronous. When the synchronous mode is selected, both the transaction tables and information structures are updated simultaneously. However, when the asynchronous mode is selected, transaction tables are updated first, and information structures later. In this case, you will not find up-to-the-second information in LIS info structures for reporting. The reason is that the R/3 system commits transaction data quickly and notifies the end user that the transaction is complete. This enables the end user to start another transaction.
But in the background, SAP R/3 delivers the LIS table update job to another dialog work process to update LIS information structures. This delay might range from a few seconds to a few minutes, depending on your system's available resources. Transaction OMO1 is used to define the synchronization scheme for a specific LIS information structure. LIS information structures are simple database tables named S001 through S499. These tables are used for reporting and analysis.
You can define your own custom information structures to capture specific data for reporting (name range S500 through S999). SAP BW pulls data from all LIS information structures defined in SAP R/3; however, the update logic for SAP BW-specific information structures varies from traditional update rules used for LIS reporting.
You can browse here about the previous post better performance achievement with data ware house
No comments:
Post a Comment